Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) Solution
Seamless and Secure Network Access to Corporate Resources

What is a Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) Solution?
A ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Access) is a network access solution that provides secure access to corporate resources, applications, and data based on strict identity verification. ZTNA stands out from the traditional network access methods by following an "Always Verify, Never Trust" principle. This makes it ideal for enabling secure remote work and protecting sensitive data.
Why Do Businesses Need a Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) Solution?
Cyber attacks are rampant, with one happening every 39 seconds¹ and over 50% of businesses² lacking visibility into unsecured WiFi on employee devices (BYOD). That’s not all; 80% of all breaches³ use compromised identities. Traditional security isn’t enough to safeguard against the latest cyber threats.
ZTNA offers a modern solution to security threats by isolating application access from the network. This protects your data even on compromised devices and ensures that only authorized users get access to specific applications.
(*¹Source-CTM file, ²Source-Cybersecurity Insiders, ³Source-CrowdStrike)
How Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is Different from Legacy Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
Choosing between Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) and legacy Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) is critical for ensuring your network’s security, scalability, and performance. Legacy VPNs, designed before the widespread adoption of cloud applications and remote work, struggle to meet the needs of modern organizations. Traditional VPNs fall short on security and privacy with their outdated encryption and user authentication methods.
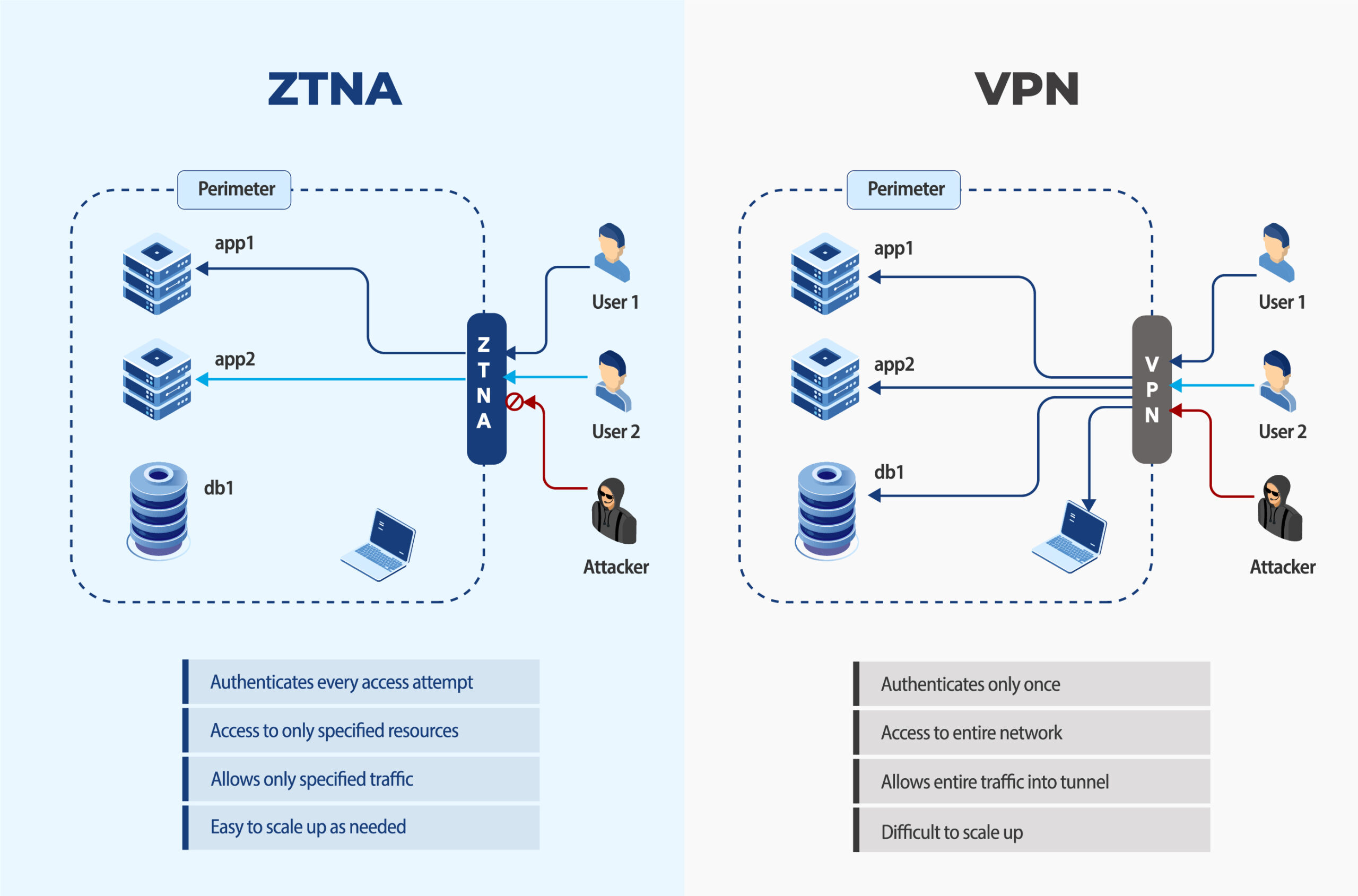
Here’s a comparison of how ZTNA and VPNs differ in key areas:

ZTNA vs VPN: Security
ZTNA grants access based on the 'Know to Access' philosophy. This means that only authorized users and devices are explicitly identified and authenticated before being granted access to resources each time. In contrast, a VPN authenticates only once at the start of the connection. This can be problematic because it potentially exposes the network to insider threats once that initial trust is established.
ZTNA vs VPN: Access Control
ZTNA restricts access to only the applications or data required, significantly reducing the attack surface. VPNs, on the other hand, grant users broad access to all corporate resources once authenticated. This can result in users having more access than necessary, posing a potential risk for compliance violations.
ZTNA vs VPN: Traffic Management
ZTNA routes only the necessary internet traffic through the tunnel, reducing wait times. In contrast, VPNs route all traffic through the corporate network, creating bottlenecks that can lead to delays and disruptions for users accessing both internal resources and external websites.
ZTNA vs VPN: Scalability
ZTNA is a cloud-based and hardware-free solution, making scalability easier as needed. Traditional VPN comes with security stacks that require expensive investments and complex management making it difficult to scale up.What are the benefits of Zero Trust Network?

Enhanced Security
ZTNA creates a secure and encrypted tunnel for network access and data transmission, preventing unauthorized access and malicious actors.

Authenticated Access
ZTNA ensures that every time access to your network is granted only to authorized devices and applications with proper security configurations, minimizing the risk of breaches each time.

Reduced Attack Surface Area
ZTNA grants access only to the required applications or data based on the configured policies, thereby reducing the attack surface in case of insider threats.


Secure BYOD Access
ZTNA ensures that personal devices accessing corporate resources adhere to security requirements through the inbuilt Zero Trust Architecture.
Work from Anywhere
ZTNA allows remote employees to access corporate resources securely from any part of the world and at any time.

Data Breach Mitigation
Internet traffic is securely tunneled through the ZTNA tunnel, eliminating the risks of data breaches and unauthorized access.
FAQs
What is VPN?
What is Zero Trust Network?
What are the differences between VPN and ZTNA solutions?
What are the three key principles of the Zero Trust Architecture?
How does ZTNA works?
Securely access your corporate resources with ZTNA
