Wearable Technology a Game Changer for BYOD?
Avr 16, 2018 | 42Gears Team
With large scale acceptance of BYOD, the use of consumer devices in enterprise ecosystems are rapidly growing. The adoption of wearables is not just limited to fitness and fashion, but has become a vital business tool. Industries such as mining, transportation, healthcare, construction, and hospitality are implementing smart technology in order to increase productivity, enhance work safety, cut cost, etc..
Wearable Technology Instances:
Smart glasses and smartwatches are two of the most widely used enterprise wearables. Other examples for wearable technology include wearable scanners, smart helmets, headbands, smart safety vest, body camera and smart t-shirts.
The enterprise wearables market is predicted to climb 500% to $55 billion revenue by 2022. Analysts believe more enterprises will adopt wearables for business purposes such as employee training, workforce access and safety.
BYOD for Wearables: What It Means for Enterprises
Design wearables for enterprise purpose only:
Originally, wearables were created for consumer purposes only, not for enterprise use. They came with short battery lives and short range transmission. They are also vulnerable to malware attacks. Rapid implementation of wearable tech in enterprise environments require businesses to invest more in making them secure, improve battery life and enhance range.
Develop customized apps for wearables and updates:
Enterprises need to develop customized apps dedicated to their needs. Wearable OS and the apps must be updated regularly to ensure that data is properly processed.
Ensure Connectivity for these devices:
Until now, the majority of wearables are connected through public networks. But as these devices are now being used for business purposes, enterprises must expand their wireless network plans and coverage to provide connectivity for remote workers as well.
Centralized tool to manage all devices:
Ability to track and manage wearable computing devices are important criteria when managing the associated risks of wearables in any business scenario. An EMM solution can enable enterprises to truly tap into the benefits of wearables by empowering them with extended control and management capabilities.
Let’s take a look at some of the use cases and benefits of wearables in different industry verticals:
Healthcare:
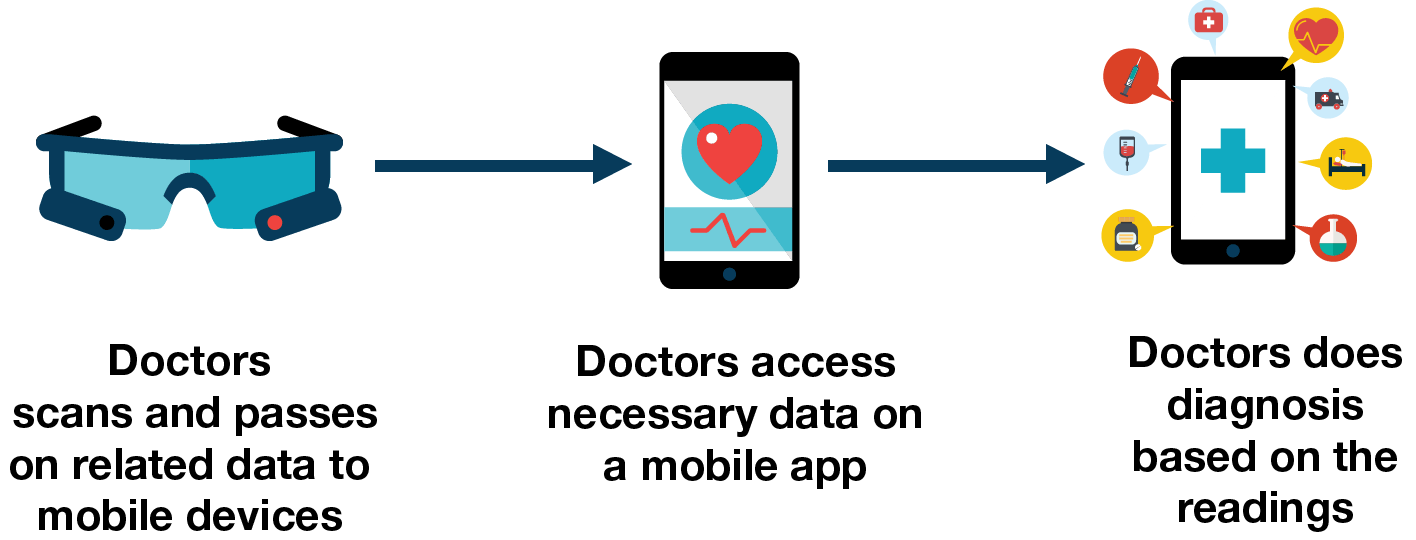
The Healthcare industry has already started using smartglasses to transmit patients’ health reports, read scans and passes on related data to their smartphones or tablets. Smartglasses, when connected via applications, can help surgeons access necessary data during the complex surgery process.
Wearable sensors are the latest advancements in the wearable segment. Apart from being effective in monitoring biological processes, wearable sensors are extremely durable, pressure-sensitive and harmless. Some advantages of wearable sensors include remote sensing and data collection. For instance, sensors in plasters can send patient recovery data to doctors, allowing the patient to return back home. Sensor-based wearables can help to assess the performance of muscles in heart stroke patients, providing real-time data. Thus, it would enable doctors to tend to multiple patients, making medical care less expensive and more accessible.
Air Travel:
Smartwatches are used as business tool in different airports to deploy various jobs directly to the workforce. In June 2015, Quebec City Lesage International Airport provided smartwatches to duty managers in order to distribute flight updates and gate changes right to their wrists. This process proved to be faster than consulting tablet computers.
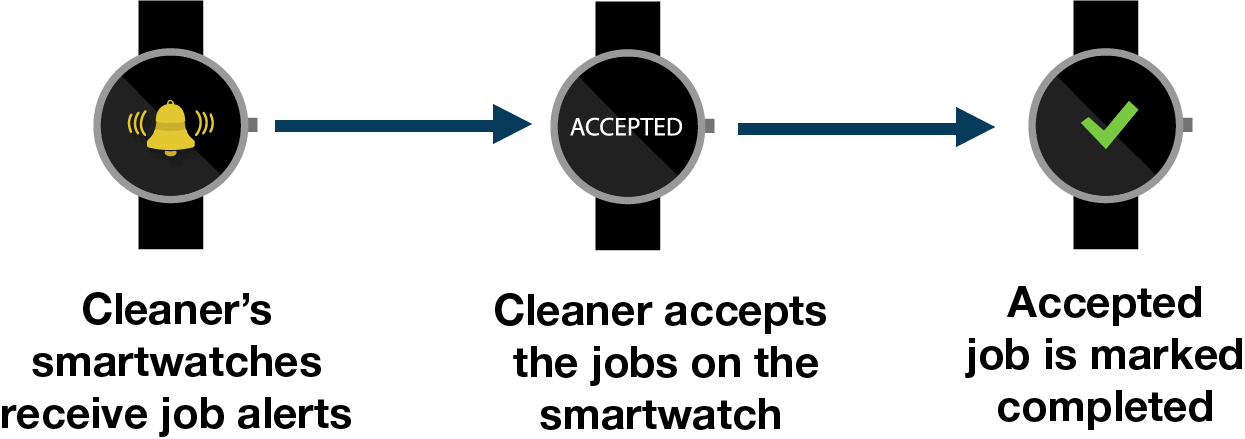
Janitors in Cincinnati Airport use smartwatches to receive job alerts whenever a restroom needs attention. The janitorial cleaners can directly accept jobs on their company-owned smartphones through an app. This helps improving the cleanliness of the airport while aiding and providing more free time to the cleaners.
Smartwatches allow airline employees of Virgin Atlantic to greet passengers by their name in the Upper-Class Wing at London Heathrow Airport. These smart devices provide real-time information about passengers, allowing the staff to commence with check-in before the passengers reach the terminal door.
This approach inspired Vueling, Iberia and Airberlin airlines to launch smartwatch boarding passes for enhanced passenger experience.
Logistics:
Businesses have started implementing wearable scanners in warehouses to streamline their inventory management process. These devices are hands-free, can be easily worn on the wrist, hip, or fingers and are connected through Bluetooth. They can reliably transmit critical data from up to 30 feet away. With wearable scanners, businesses can not only lower cost of ownership, but also reduce device downtime. Being lightweight and durable, these devices allow warehouse workers to use both hands for picking and sorting instead of holding their devices. This helps to reduce counting errors, boost efficiency, cut labor and hardware costs.
Field Service:
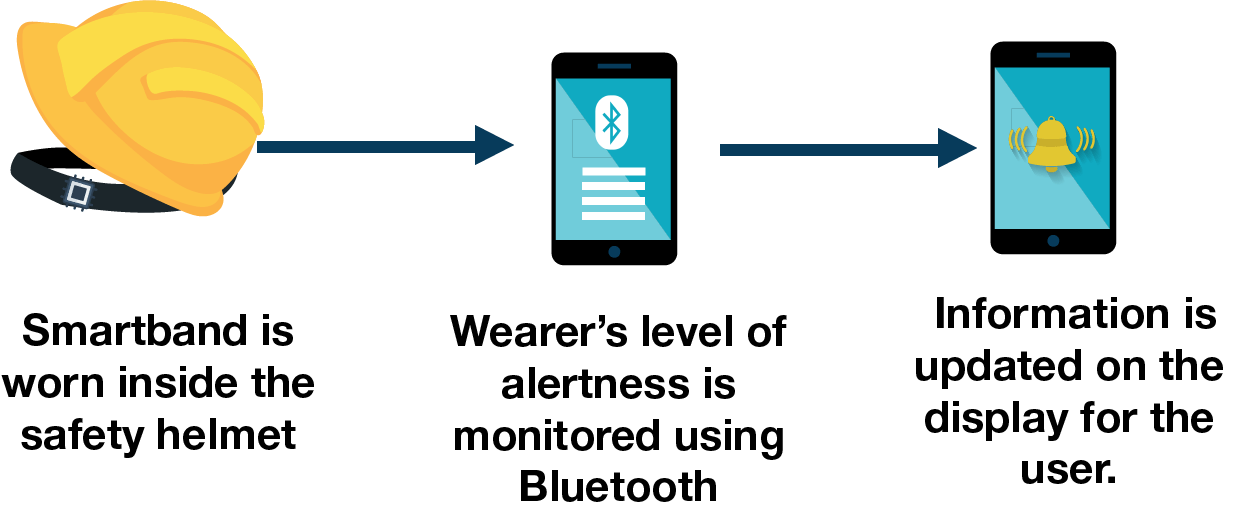
Wearables are also used by fleet-based businesses for detecting signs of worker fatigue. Wearables in the form of bands can be worn with beanie, cap or safety helmet. This technology was successfully developed by SmartCap, (an Australian cloud-based fatigue monitoring solution provider) using electroencephalography to measure brain waves. The sensors in the band determine the wearer’s level of alertness every second. Alertness or fatigue information is displayed through an app on a Bluetooth-enabled device (such as PDA, mobile phone or display) carried by the users. In case there is no confirmed level of fatigue within two minutes, the information is updated in the display for the user. This innovation is helpful especially for operators of heavy machinery to prevent accidents in the field. The technology is completely non-intrusive, flexible and low in cost.
High-Risk Field Operations:
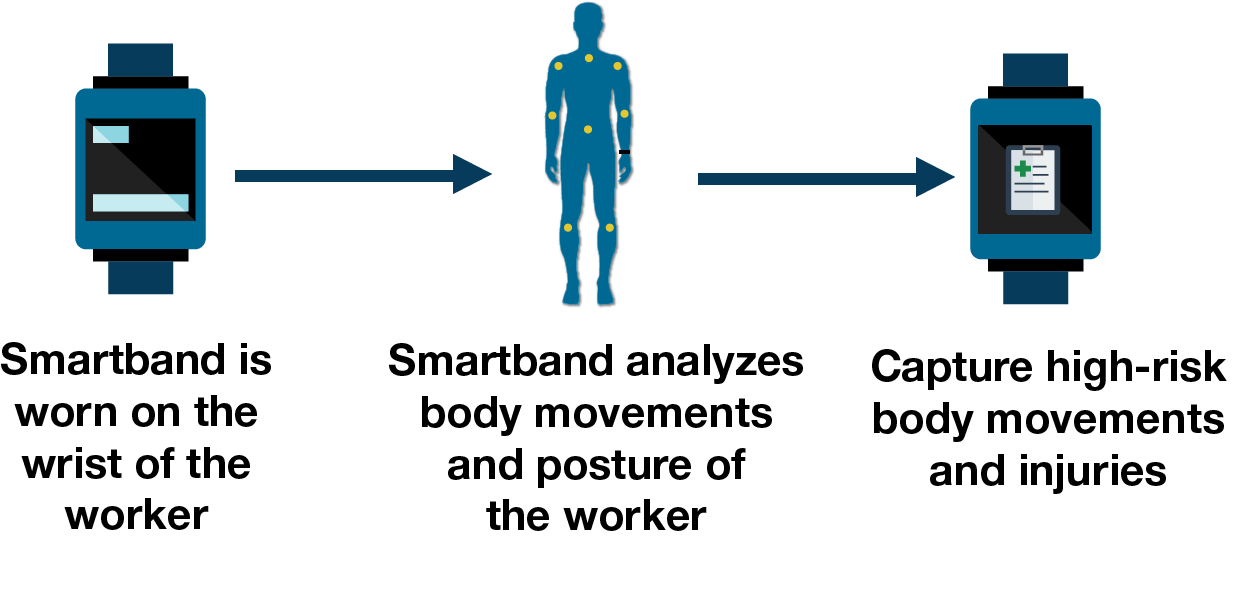
Wearables can provide real-time notifications about workplace safety in high-risk or hazardous locations such as oil rigs, mines, wind turbines and construction sites, thus preventing accidents on site. Wearable sensors can analyze the body movements and posture of warehouse workers while they undertake manual tasks. They can capture movements like bending, reaching, and twisting to reduce the risk of back and shoulder injuries.
The greatest advantage of wearables is the ability to allow users performing tasks handsfree. This feature is beneficial for field workers as they can store biometric data in the wearables for access control such as opening doors.
Integrating wearables in enterprise workflow can improve worker efficiency and productivity while making the workplace safer and more secure. However, most enterprises are yet to realize the full potential of wearable technology, including the ability to automate business processes and monitor various workplace scenarios.
Using an UEM solution such as SureMDM, admins can remotely push apps and updates to Android wearables.
Interested to know more about Wearable Management features offered by 42Gears EMM? Click here for a free trial.
Subscribe for our free newsletter