A Comprehensive Guide on Linux Patch Management and its Best Practices
Okt 17, 2024 | Nareddy Saivikas Reddy
If you are system administrator or IT manager an effective Linux patch Management strategy is crucial to keep Linux devices running smoothly and securely. You play a crucial role in ensuring that all Linux systems within your organization are up to date with the latest patches and updates. To maintain optimal security and performance, system administrators need to master the process of identifying and deploying the latest patches across enterprise Linux devices.
In this blog, we will explore linux patch management, and discuss how linux device management solution can help you effectively manage and update your Linux devices.
What is Linux Patch Management?
In the world of Linux, patch management involves applying patches to those little snippets of code that fix bugs, resolve security vulnerabilities, or add features. According to a study, 57% of companies1 that have experienced data breaches say these breaches could have been prevented by applying a patch to a known vulnerability or implementing effective linux patch management strategy.
Think of patching as regular check-ups for your devices; they help keep everything in peak performance and keep your devices secure and efficient. Patch management in Linux can be a complex task, but with the right Linux patch management solution like SureMDM, it is made easy.
Why is Linux Patching Important?
Linux patching is crucial for maintaining device security and stability. Regular updates address vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers, protecting sensitive data and infrastructure. Patching also ensures compatibility with new applications and hardware, enhancing overall performance. Also, keeping devices up-to-date helps organizations comply with industry regulations and standards. Ultimately, proactive patch management minimizes downtime and reduces the risk of costly security incidents.
How Often Should Linux Patches Be Applied for Optimal Security?
Patch management should be performed regularly to ensure system security and stability. However, the frequency may vary depending on the organization's needs and the type of patches:
- Critical Security Patches: Apply as soon as possible, ideally within a week or two of release. For some high priority patches, it is required to apply patches within 24 to 48 hours of release.
- Non-Critical Updates: Apply monthly or as part of a scheduled maintenance window.
Regular reviews and monitoring are essential to address vulnerabilities and maintain system stability.
Common Challenges in Linux Patch Management
- Good patches can go bad: Patches can conflict with certain applications on the devices, leading to unexpected behavior, system instability, and potential incompatibility with specific hardware configurations that may result in errors or performance degradation.
- Lack of visibility: Managing a large number of patches can overwhelm IT teams, making it difficult to track which devices are up to date. This lack of visibility can delay the identification of devices that failed to apply patches, leaving them exposed to security risks.
- Resource constraints: Many IT teams struggle with limited time and personnel to keep up with the patching schedule, especially as the number of devices grows. Limited resources can lead to delays, missed patches, and increased administrative overhead.
- End-user interference and downtime: Users may delay or cancel patch installations, especially during non-critical updates, leading to vulnerabilities and system inconsistencies.
Security and Compliance Risks: In industries such as healthcare and finance, regulatory standards require organizations to keep their systems up-to-date. Failing to apply the latest security patches can result in compliance issues and increase the risk of data breaches or cyber-attacks.
What Does a Linux Patch Management Tool Do?
Linux Patch Management Tools like SureMDM provide a centralized patch management for security and functional updates across major Linux distributions, including Ubuntu, Fedora, and Linux Mint. In SureMDM, whenever a new patch is released, it will be discovered and added to the ‘OS Updates’ section for validation and approval. The SureMDM agent then scans for eligible devices for the applicable patches, making the system administrator's job easier to identify and deploy the accurate patches onto the devices.
SureMDM empowers administrators to establish compliance policies tailored to specific Linux versions. These policies automatically enforce actions such as applying updates, blocking non-compliant devices, or locking them when they fail to meet defined criteria. By implementing these measures, organizations can ensure that all devices consistently adhere to their security standards, safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining overall system integrity.
Learn how to apply patches on Linux devices
Take a look at the Linux Patch Management feature on your console
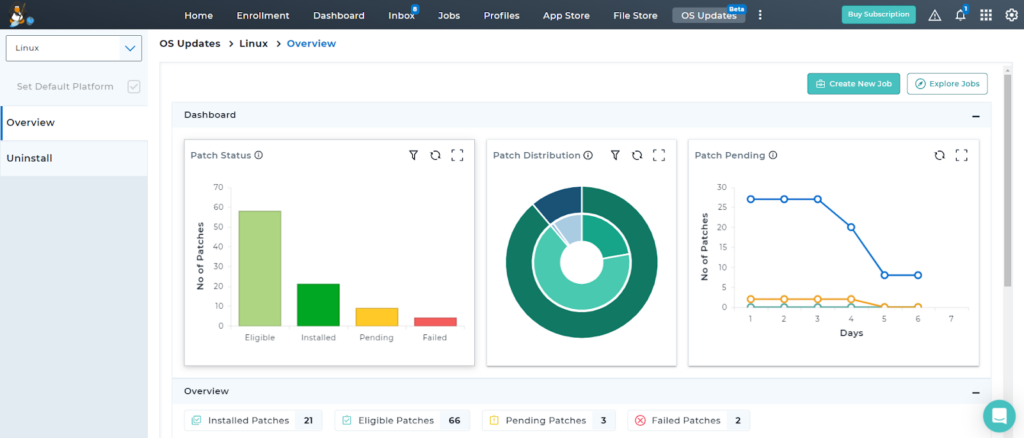
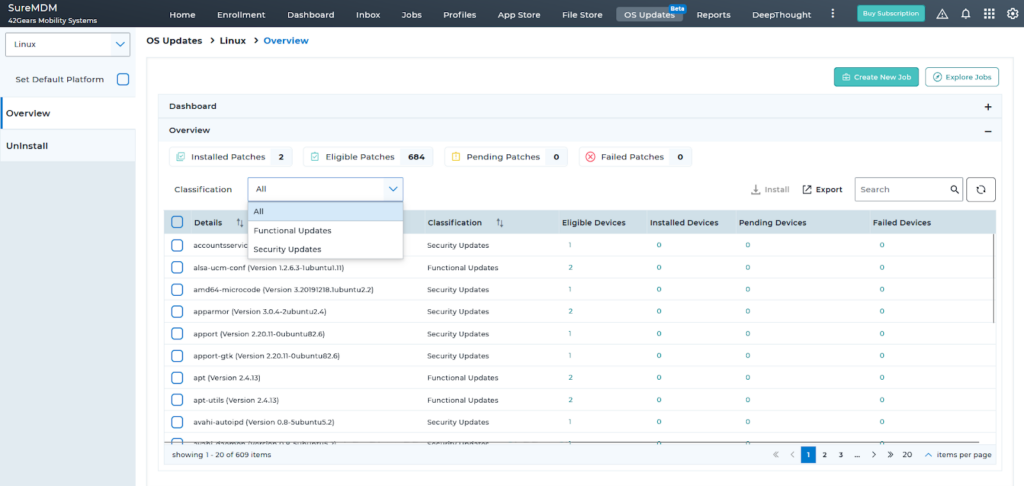
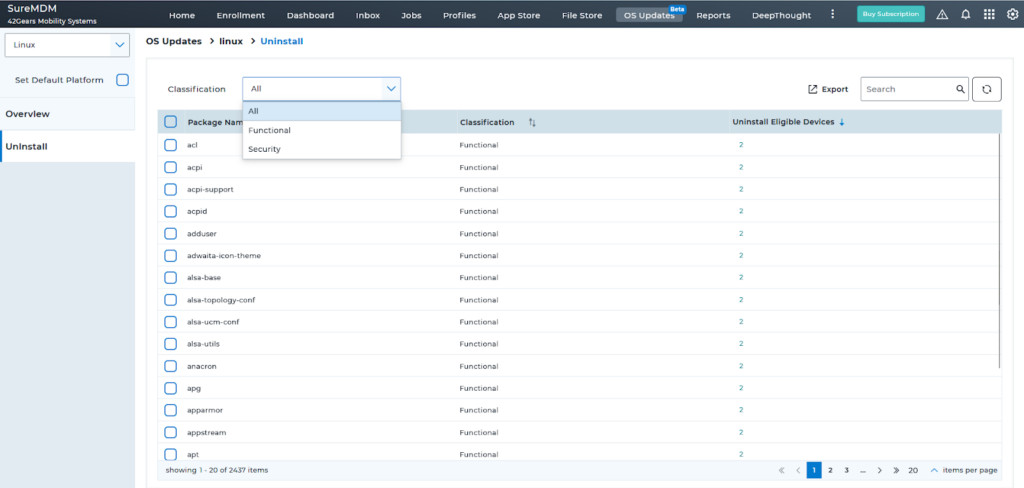
Learn more about the critical metrics for effective patch management with SureMDM
Best Practises of Linux Patch Management
- Monitor your devices for any bug fixes, functional or security patches and update regularly to protect from known vulnerabilities,
- Prioritize patches by evaluating the potential risks and impacts of applying them, ensuring both security and system stability.
- Test patches on a small number of devices to identify any compatibility issues and unexpected behaviours before deploying patches on a large number of devices.
- Configure patch management settings to enable a continuous process of monitoring, testing, and patch deployment, ensuring efficient collaboration and reducing ambiguity.
- Have a centralized patch management solution to automate deployment, reduce manual effort, and provide centralized control and visibility across systems.
- Keep records of installed patches for audit and compliance.
- Train your staff on the importance of timely patching, risks with delayed patching, and best practices of patch management.
Benefits of Choosing SureMDM for Linux Patch Management
- Patch the exposed vulnerabilities on your Linux devices, keeping them secured.
- Reduce IT workload, save time and money by automating the entire patching process—monitoring, deploying patches, and providing detailed insights through a dashboard.
- Easily manage patching for a growing number of Linux devices without additional resources.
- Ensure uniform patching across all devices.
- Centralized Linux Patch Management solution for all supported Linux distributions.
To Sum It Up
SureMDM streamlines the Linux patching ensuring device security and stability. Along with Linux patching, SureMDM also supports OS update and patch management for Windows, iOS and macOS devices.
(*¹Source-Ponemon Institute)
Simplify Linux patching with
SureMDM
Subscribe for our free newsletter


